FPC Electronics to See Increased Demand with Rising Wearable Technology Market
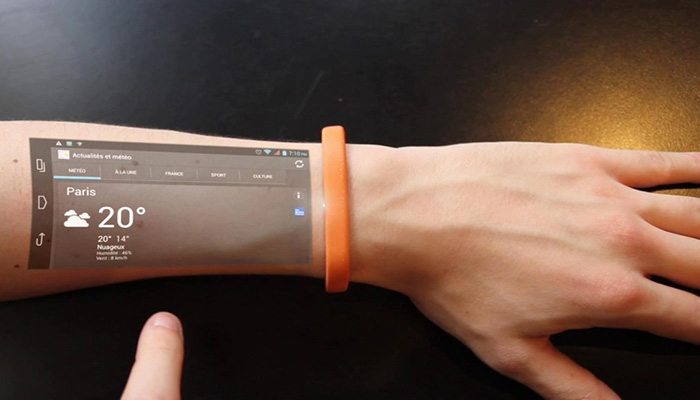

Wearable technology with sensing functionality is emerging as a highly promising application for printed/flexible electronics. Deployed either as skin patch or embedded within an e-textile, these devices enable parameters such as heart rate and temperature to be recorded in real-time and then transmitted wirelessly. With such clear benefits, IDTechEx estimate that the wearable skin patch market for healthcare applications will reach around $ 4 billion by 2030. Printed/flexible electronics is extremely well suited to wearable skin patches due to its low weight, flexibility/conformity and potential for high-throughput, low-cost manufacturing of these disposable items.
Need for Continuous Monitoring
A major trend in the healthcare sector is a shift towards continuous monitoring, which brings multiple benefits. Firstly, rather than attending a doctor's surgery or hospital for a check-up, the patient can remain at home. The current COVID-19 situation has emphasized this benefit since patients can have their temperature measured remotely without having to interact with healthcare professionals and thus risk transmitting or acquiring the virus. An additional benefit is that continuous monitoring enables data to be acquired with a far higher temporal resolution than would be possible with in-person visits since a skin patch can be worn at all times. This additional data, coupled with analysis via machine learning, should facilitate improved diagnosis and preventative medicine.
Monitoring Electrical Signals
Monitoring electrical signals is an important use case for wearable skin patches. This can include electrocardiograms (ECG) for investigating the heart, electromyography (EMG) for recording electrical signals from muscles, and even detecting brain activity in epileptic patients.
These are typically manufactured using screen-printed stretchable conductive inks and electrodes, with the latter made from a mixture of silver and silver chloride. Conductive traces are typically printed in a wave-like pattern to increase stretchability, while most of the electronics are currently contained in a rigid case. Electrodes and conductive traces are also being integrated within e-textiles, either on a stretchable substrate that is subsequently attached or printed directly onto the fabric.
Pressure and Strain Sensing
Aside from monitoring electrical signals, both pressure and strain can be measured using printed/flexible sensors. For example, incorporating a conformal thin film piezoresistive sensor can continuously measure the pressure being applied by bandages and alert medical staff if the bandage needs adjusting. Maintaining an appropriate pressure is important: too loose and it is entirely pointless, too tight and it unnecessarily restricts blood flow to the affected region. Another application being trialed is monitoring joint movement using printed capacitive strain sensors incorporated, for example, into knee and elbow sleeves. This is useful for those receiving physiotherapy since the amount and extent of movement can be continuously assessed.
Extensive Opportunities in Wearable Technology for Printed/Flexible Sensors
To summarize, the transition towards continuous healthcare monitoring and interest e-textiles for fitness tracking provide substantial opportunities for printed/flexible electronics. This includes both printed sensors to detect the biological parameters and flexible hybrid electronics to process the signals and handle wireless communication.

 Send Email
Send Email 15889340690
15889340690